My submission to EmacsConf 2025 has been accepted. Hopefully by then I'll have all the bugs and some basic features finalized.
https://emacsconf.org/2025/talks/reader/
https://emacsconf.org/2025/talks/reader/
Forwarded from A Math Book
Logic machines and diagrams.pdf
9.2 MB
Logic Machines and Diagrams ( Martin Gardner ). McGraw-Hill 1958
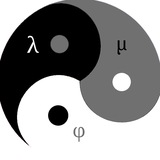
(φ (μ (λ)))
https://youtu.be/SphBW9ILVPU
YouTube
Dana S. Scott: Seventy Years Using Fixed Points
Title: Seventy Years Using Fixed Points
Speaker: Dana S. Scott
Abstract: Having first heard about theorems on fixed points as an undergraduate, uses for them came into my research on many subsequent occasions. The talk will review some personal history and…
Speaker: Dana S. Scott
Abstract: Having first heard about theorems on fixed points as an undergraduate, uses for them came into my research on many subsequent occasions. The talk will review some personal history and…
(φ (μ (λ)))
Live stream finished (2 hours)
Dyne.org TV
[10] Emacs Reader's Development: Working on Partial & Tiled Rendering - 8/24/2025, 3:42:15 PM
This is the ninth in a series of Emacs package development streams focusing on the Emacs Reader package: https://codeberg.org/divyaranjan/emacs-reader/ In this stream specifically, I'll be sharing ...
(φ (μ (λ)))
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kerckhoffs%27s_principle
Katz & Lindell, Introduction to Modern Cryptography (2007)
Forwarded from A Math Book
The Art of Differentiating Computer Programs.pdf
1.3 MB
The Art of Differentiating Computer Programs: An Introduction to Algorithmic Differentiation ( Uwe Naumann ). SIAM 2012
Forwarded from ilo sona
This media is not supported in your browser
VIEW IN TELEGRAM
Why memory fragmentation matters.
This is the result of a random sequence of memory allocations and frees wherein the allocator uses a first-fitting-free-block algorithm. The sequence is randomly generated to issue an alloc or free call every 0.01 seconds, with a 60% bias towards allocating memory. Each allocation requests a randomly generated size between 2 and 18 bytes. The program stops when the page is full.
This is the result of a random sequence of memory allocations and frees wherein the allocator uses a first-fitting-free-block algorithm. The sequence is randomly generated to issue an alloc or free call every 0.01 seconds, with a 60% bias towards allocating memory. Each allocation requests a randomly generated size between 2 and 18 bytes. The program stops when the page is full.
One of the several conjectures that'll be solved with P vs. NP:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One-way_function
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/One-way_function
Wikipedia
One-way function
In computer science, a one-way function is a function that is easy to compute on every input, but hard to invert given the image of a random input. Here, "easy" and "hard" are to be understood in the sense of computational complexity theory, specifically…